Quick Betimate
Popular Leagues
-
UEFA Nations League
-
England (22)
- FA Cup
- Premier League (9)
- Championship (1)
- League 1 (1)
- League 2 (1)
- National League (2)
- National League North (1)
- National League South (1)
- EFL Trophy
- Premier League 2
- Championship Women
- Development League 2 (1)
- FA Cup Women (1)
- FA Trophy
- FA Vase
- Isthmian Division One North
- Isthmian Division One South
- Isthmian Premier Division
- National League Cup
- Northern League Division One
- Northern Premier League
- Reserve Matches
- Southern Premier League Central
- Southern Premier League South
- Super League Women
- U21 Premier League Cup
- Northern Ireland Championship
- Northern Ireland Championship Women
- Northern Ireland Cup
- Northern Ireland Intermediate Cup
- Northern Ireland League Cup Women
- Northern Ireland Play-Offs
- Northern Ireland Premier
- Northern Ireland Premier Intermediate League
- Northern Ireland Premier League Women (4)
- Northern Ireland Reserve League
- Scotland Regional Cup
- Wales League Cup Women
-
Japan J-League Cup (7)
-
UEFA Champions League (1)
-
Spain (107)
- La Liga (10)
- Segunda (5)
- Tercera Group 1 (2)
- Tercera Group 2 (3)
- Tercera Group 3 (2)
- Tercera Group 4 (2)
- Tercera Group 5 (2)
- Tercera Group 6 (2)
- Tercera Group 7 (2)
- Tercera Group 8 (2)
- Tercera Group 9 (2)
- Tercera Group 10 (2)
- Tercera Group 11 (2)
- Tercera Group 12 (2)
- Tercera Group 13 (2)
- Tercera Group 14 (2)
- Tercera Group 15 (2)
- Tercera Group 16 (4)
- Tercera Group 17 (3)
- Tercera Group 18 (2)
- Youth League
- Copa De La Reina (1)
- Copa del Rey
- Kings League - 40 mins play (1)
- Primera Division RFEF Group 1 (10)
- Primera Division RFEF Group 2 (10)
- Primera Federacion Women (1)
- Primera Women
- Queens League - 40 mins play
- Regional Cup
- Regional League
- Segunda Division RFEF Group 1
- Segunda Division RFEF Group 2
- Segunda Division RFEF Group 3
- Segunda Division RFEF Group 4
- Segunda Division RFEF Group 5
- Segunda Division RFEF Play-Offs (10)
- Segunda Federacion Women
- Tercera - Play-Offs (19)
- Tercera Federacion Women
- Women Regional League
-
USA (795)
-
UEFA Europa League (1)
-
Germany (74)
- Bundesliga I
- Bundesliga II (9)
- DFB Pokal (1)
- Regionalliga Bayern
- Regionalliga North (3)
- Regionalliga North East (8)
- Regionalliga South West
- Regionalliga West
- Oberliga Baden-Wuerttemberg (1)
- Oberliga Bayern North
- Oberliga Bayern South
- Oberliga Bremen
- Oberliga Hamburg
- Oberliga Hessen (1)
- Oberliga Mittelrhein (6)
- Oberliga Niederrhein (8)
- Oberliga Niedersachsen (9)
- Oberliga NOFV Nord (2)
- Oberliga NOFV Sud (8)
- Oberliga Rheinland-Pfalz/Saar (5)
- Oberliga Schleswig-Holstein
- Oberliga Westfalen (5)
- 3. Liga
- Bundesliga II Play-Offs
- Bundesliga II Women (7)
- Bundesliga Play-Offs
- Bundesliga U19
- Bundesliga Women
- DFB Pokal Women
- Regionalliga Play-Offs
- U19 Cup (1)
-
Italy (34)
- Serie A (9)
- Serie B (1)
- Serie C Group A
- Serie C Group B
- Serie C Group C
- Campionato Nazionale
- Campionato Primavera 1 (2)
- Campionato Primavera 2 (2)
- Serie D (3)
- Coppa Italia
- Coppa Italia Women
- Campionato Primavera 3
- Campionato Primavera 4
- Serie A Women
- Serie B Play-Offs (4)
- Serie B Women (1)
- Serie C Play-Offs (4)
- Serie C Super Cup
- Serie D Play-Offs (8)
- U19 League Women
-
France (15)
-
Netherlands (25)
-
Scotland (10)
-
Japan J-League (2)
-
Denmark Superligaen (5)
-
Cyprus Division 1 (3)
-
Israel Premier League (2)
-
Colombia Primera A (5)
-
Indonesia Liga 1 (2)
-
Colombia Primera B (7)
-
Esport (68)
Other Leagues
-
Albania
-
Algeria (5)
-
Andorra (5)
-
Angola (4)
-
Argentina (80)
- Nacional B (10)
- Primera B Metropolitana (7)
- Primera C Metropolitana (11)
- Reserve League
- Cup (11)
- Torneo A (15)
- Copa Santa Fe
- Championship Women (7)
- Copa de la Liga Profesional
- Copa Santa Fe Women
- Liga Profesional (4)
- Liga Profesional Reserves (15)
- Nacional Reserve League
- Regional League
- Youth League
-
Armenia (8)
-
Aruba (3)
-
Australia (119)
- A-League (2)
- A-League Women
- Capital Territory NPL2 (4)
- Capital Territory NPL2 U23 League
- Capital Territory Premier League (4)
- Capital Territory Premier League Women
- Capital Territory Premier League Women Reserves
- Capital Territory U23 League
- Cup
- Cup Qualifying
- Darwin Premier League
- FFA Cup Qualifying
- New South Wales League 1 (8)
- New South Wales League 2
- New South Wales NPL Women (7)
- New South Wales NPL2 Women
- New South Wales Premier League (8)
- New South Wales U20 League (1)
- Northern NSW Division 1 (1)
- Northern NSW Premier League (2)
- Northern NSW Premier League Women
- Northern NSW Reserves League
- NPL Queensland (6)
- NPL Queensland U23
- NPL Queensland Women (5)
- NPL Victoria (7)
- NPL Victoria U23 (1)
- NPL Victoria Women (6)
- NSW League 1 U20
- NSW League 2 U20
- Queensland PL 2 U23
- Queensland PL U23
- Queensland Premier League (6)
- Queensland Premier League 2 (6)
- Queensland Premier League 2 Women
- Queensland Premier League 3
- Queensland Premier League 4
- Queensland Premier League Women
- SA Premier League Reserves
- SA Premier League Women (5)
- SA Premier League Women Reserves
- South Australia Premier League (6)
- South Australia State League 1 (6)
- South Australia State League Reserves
- Sunday League Premier Division
- Sunday League Premier Division Reserve
- Tasmania Championship (4)
- Tasmania Championship 1
- Tasmania Championship Women
- Tasmania NPL U21 League
- Tasmania Premier League (4)
- Tasmania South Division 1
- Tasmania Super League Women
- Victoria PL 1 U23
- Victoria Premier League 1 (7)
- Victoria Premier League 2
- Victoria Premier League Women
- Victoria State League 1
- Victoria State League 1 Reserves
- Victoria State League 2
- Victoria State League 2 Reserves
- WA Premier League Women (1)
- WA Premier League Women U21
- WA State Cup Women
- WA State League 1 Reserves
- Western Australia Premier League (6)
- Western Australia State League 1 (6)
- Western Australia State League 1 Women
- Western Australia State League 2
- Western Australia U23 League
- Australian Matches
-
Austria (37)
-
Azerbaijan (8)
-
Bahrain
-
Bangladesh (5)
-
Barbados (2)
-
Belarus (7)
-
Belgium (4)
-
Benin
-
Bhutan
-
Bolivia (14)
-
Bosnia & Herzegovina (11)
-
Botswana (8)
-
Brazil (176)
- Serie A (7)
- Serie B (5)
- Serie C (6)
- Campeonato Amapaense
- Campeonato Baiano 2 (3)
- Campeonato Brasileiro A2 Women (3)
- Campeonato Brasileiro Serie B U20 (4)
- Campeonato Carioca A2 (1)
- Campeonato Carioca B (6)
- Campeonato Goiano 2 (4)
- Campeonato Maranhense
- Campeonato Mineiro 2 (6)
- Campeonato Mineiro U20 (3)
- Campeonato Paranaense 2 (2)
- Campeonato Paulista A4
- Campeonato Paulista U20 (3)
- Catarinense 2 (4)
- Copa Espirito Santo (4)
- Copa Nordeste (4)
- Copa Rio Women
- Copa Verde
- Matches
- Matches Women
- Paraense
- Paulista Cup (11)
- Paulista Serie B (4)
- Paulista Women (4)
- Serie A U20 (10)
- Serie A1 Women (5)
- Serie A2 Women (1)
- Serie A3 Women (12)
- Serie D (20)
- U20 Cup
- U20 League (28)
- U20 Women Cup
- Copa do Brasil (16)
- Women’s Friendly
-
Bulgaria (6)
-
Burkina Faso
-
Burundi
-
Cambodia (3)
-
Cameroon (8)
-
Canada (8)
-
Chile (12)
-
China (38)
-
Colombia (15)
-
Costa Rica (3)
-
Côte d’Ivoire (8)
-
Croatia (16)
-
Cuba
-
Cyprus (3)
-
Czech Republic (47)
-
Denmark (43)
-
Djibouti
-
Dominica (2)
-
Dominican Republic
-
Ecuador (15)
-
Egypt (16)
-
El Salvador (2)
-
Estonia (12)
-
Ethiopia (4)
-
Faroe Islands (12)
-
Fiji
-
Finland (107)
-
Gambia (7)
-
Georgia (10)
-
Ghana (8)
-
Gibraltar
-
Greece (7)
-
Guatemala (3)
-
Haiti (5)
-
Honduras (2)
-
Hong Kong SAR China (5)
-
Hungary (31)
-
Iceland (34)
-
India (1)
-
Indonesia (2)
-
Iran (11)
-
Iraq (10)
-
Ireland (15)
- Republic of Ireland FAI Cup (2)
- Republic of Ireland FAI Intermediate Cup
- Republic of Ireland First Division (5)
- Republic of Ireland Leinster Senior Cup
- Republic of Ireland Leinster Senior League
- Republic of Ireland Munster Senior League
- Republic of Ireland National League Women (6)
- Republic of Ireland Premier Division (2)
- Republic of Ireland U20 League
-
Israel (11)
-
Jamaica (2)
-
Japan (58)
-
Jordan
-
Kazakhstan (12)
-
Kenya (8)
-
Kuwait (5)
-
Kyrgyzstan (1)
-
Latvia (9)
-
Lebanon (5)
-
Liechtenstein (1)
-
Lithuania (15)
-
Luxembourg (17)
-
Macau SAR China
-
Macedonia (11)
-
Malawi (9)
-
Malaysia
-
Mali
-
Malta (1)
-
Mauritania (2)
-
Mexico (7)
-
Moldova (6)
-
Mongolia
-
Montenegro (10)
-
Morocco (9)
-
Mozambique (1)
-
Myanmar (Burma)
-
Namibia
-
Nepal
-
New Zealand (16)
-
Nicaragua (1)
-
Niger
-
Nigeria (11)
-
Norway (99)
- Eliteserien (8)
- Division 1 (8)
- Cup (8)
- Cup Women (8)
- Division 1 Play-Offs
- Division 1 Women (6)
- Division 2 Group 1 (7)
- Division 2 Group 2 (7)
- Division 2 Group 3
- Division 3 Group 1 (7)
- Division 3 Group 2 (7)
- Division 3 Group 3 (7)
- Division 3 Group 4 (7)
- Division 3 Group 5 (7)
- Division 3 Group 6 (7)
- Interkretsserie U19
- Toppserien Women (5)
- U19 Elite League
- Youth Cup
-
Oman (1)
-
Panama (3)
-
Paraguay (17)
-
Peru (16)
-
Philippines
-
Poland (29)
-
Portugal (7)
-
Puerto Rico (1)
-
Qatar
-
Romania (35)
-
Russia (24)
-
Rwanda (2)
-
Saint Kitts and Nevis (1)
-
San Marino (1)
-
Saudi Arabia (20)
-
Senegal (6)
-
Serbia (10)
-
Seychelles
-
Sierra Leone (3)
-
Singapore (4)
-
Slovakia (14)
-
Slovenia (7)
-
Solomon Islands
-
South Africa (9)
-
South Korea (13)
-
Suriname (1)
-
Sweden (58)
- Europe Friendlies
- Allsvenskan Qualification
- Superettan Qualification
- 1.div Norra (3)
- Cup (1)
- 1.div Södra (2)
- 2.div Norra Götaland (1)
- 2.div Norra Svealand (2)
- 2.div Norrland (2)
- 2.div Södra Götaland (3)
- 2.div Södra Svealand (4)
- 2.div Västra Götaland (3)
- Allsvenskan (8)
- Cup Qualification (6)
- Cup Women (1)
- Damallsvenskan (1)
- Div 1 Relegation (8)
- Elitettan (4)
- Juniorallsvenskan (7)
- Superettan (2)
-
Switzerland (21)
-
Taiwan
-
Tajikistan
-
Tanzania (9)
-
Thailand (6)
-
Togo (4)
-
Trinidad and Tobago (2)
-
Tunisia (17)
-
Turkey (19)
- Türkiye 1 Lig (2)
- Türkiye 2 Lig Beyaz
- Türkiye 2 Lig Kirmizi
- Türkiye 2.Lig Play-offs (4)
- Türkiye 3. Lig Promotion Group Play-off (2)
- Türkiye 3.Lig Group 1 (1)
- Türkiye 3.Lig Group 2
- Türkiye 3.Lig Group 3
- Türkiye 3.Lig Group 4 (1)
- Türkiye Cup
- Türkiye Super Lig (8)
- Türkiye U19 League (1)
- Türkiye Womens League
-
Uganda (4)
-
Ukraine (18)
-
United Arab Emirates (14)
-
Uruguay (26)
-
Uzbekistan (8)
-
Venezuela (12)
-
Vietnam (9)
-
Wales (1)
-
Zambia
-
Zimbabwe (1)
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Basketball Positions

I. Introduction
The concept of positions in basketball originated in the early 1900s, as the sport evolved and became more organized. At the time, the game was divided into two basic positions, known as "guards" and "forwards." As the sport continued to grow and become more complex, more specialized positions emerged, such as the "center" position.
Today, there are five main different basketball positions: point guard, shooting guard, small forward, power forward, and center. Each position has its own unique role and skill set, and understanding the differences between them is essential to playing the game effectively. We will explain basketball positions in the following for you to have an overall understanding of “ what are the basketball positions ?”
The point guard is typically the team's primary ball handler and playmaker. They are responsible for bringing the ball up the court, setting up plays, and creating scoring opportunities for their teammates. Point guards are often the shortest players on the team, but they make up for their lack of height with their speed and agility.
The shooting guard is usually the team's best perimeter shooter and scorer. They are responsible for making shots from beyond the arc, as well as mid-range jumpers and layups. Shooting guards also play a key role in defending the opposing team's perimeter players.
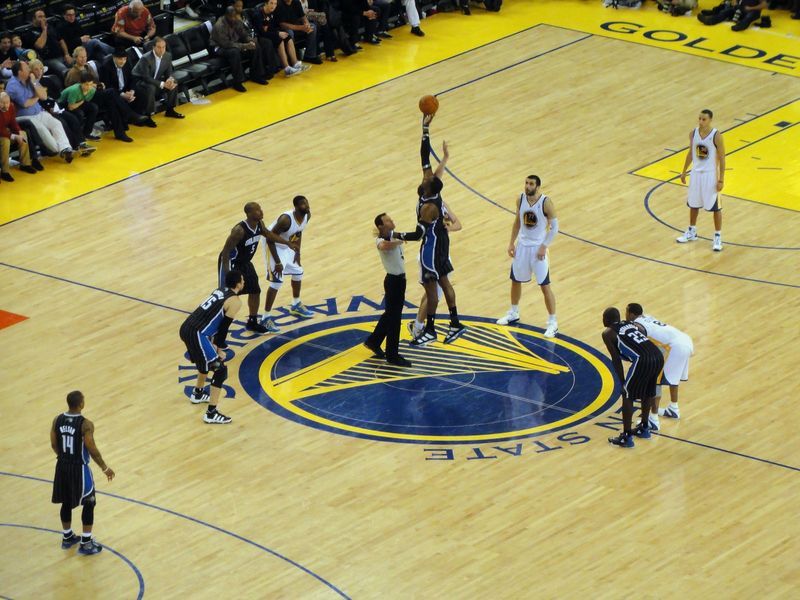 Basketball is one of the most famous sport in the world
Basketball is one of the most famous sport in the world
The small forward is often a versatile player who can contribute to the team in a variety of ways. They are responsible for scoring, rebounding, and defending, and often play a key role in transition offense and defense.
The power forward is typically a strong, physical player who excels at rebounding and scoring inside the paint. They are also responsible for defending the opposing team's power forwards and centers, and often play a key role in setting screens and running pick-and-rolls.
The center is usually the tallest player on the team and is responsible for defending the basket and rebounding. They are also responsible for scoring inside the paint and setting screens for their teammates. Centers are often skilled at blocking shots and altering their opponents' shots.
In addition to understanding the different basketball positions, it is important to have a basic understanding of offensive and defensive strategies in basketball. On offense, teams use a variety of plays and strategies to score points, including pick-and-rolls, isolation plays, and fast breaks. On defense, teams use a variety of strategies to stop their opponents from scoring, including man-to-man defense, zone defense, and full-court press.
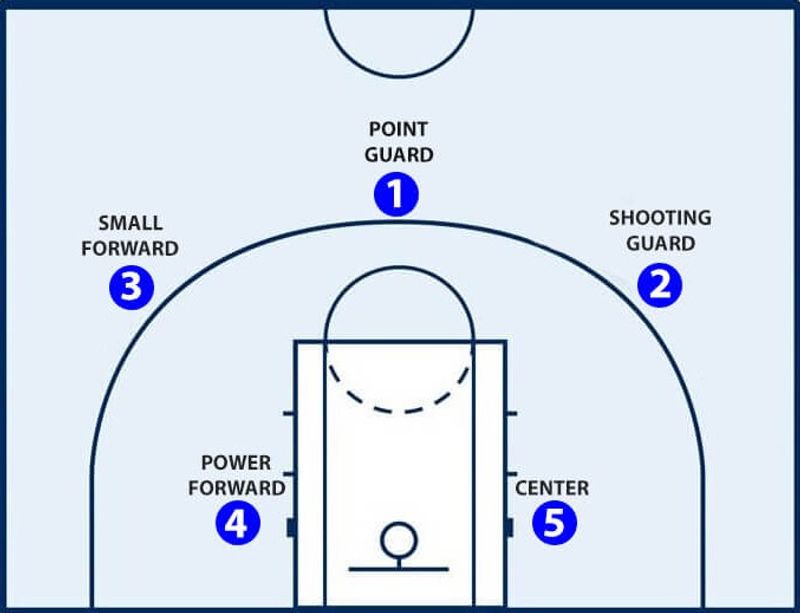 The 5 main basketball positions
The 5 main basketball positions
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of basketball positions and roles, including their responsibilities, strengths, and weaknesses. It also covers basic offensive and defensive strategies, as well as tips for improving individual skills and team performance. Whether you are a seasoned player, a new fan, or simply interested in learning more about this exciting sport, understanding all basketball positions and strategies is crucial to enjoying and succeeding in the game. By utilizing the information on all basketball positions, you will be well on your way to becoming a more knowledgeable and effective basketball player, coach, or fan.
II. The Five Traditional Basketball Positions
A. Point Guard
The point guard position in basketball is an important role that is responsible for directing the team's offense and defense. Point guards are often the shortest players on the team, but they make up for their lack of height with their speed, agility, and quick decision-making abilities. They are typically the primary ball handlers and playmakers on the court, and they must possess exceptional ball-handling skills and court vision to create scoring opportunities for their teammates.
On offense, the point guard is responsible for bringing the ball up the court, setting up plays, and creating scoring opportunities for their teammates. They must be able to read the defense, make quick decisions, and execute passes with precision. Point guards often run pick-and-rolls, where they use a screen from another player to get free and drive to the basket, shoot a jump shot, or pass to an open teammate. They may also run isolation plays, where they take on a defender one-on-one or set up off-ball screens to create open shots for their teammates.
On defense, the point guard is responsible for pressuring the opposing team's ball handler and disrupting their offensive flow. They must use their quickness and agility to stay in front of their opponent and prevent them from getting open shots. Point guards often play a key role in trapping and double-teaming opposing players, especially if they are primary scorers.
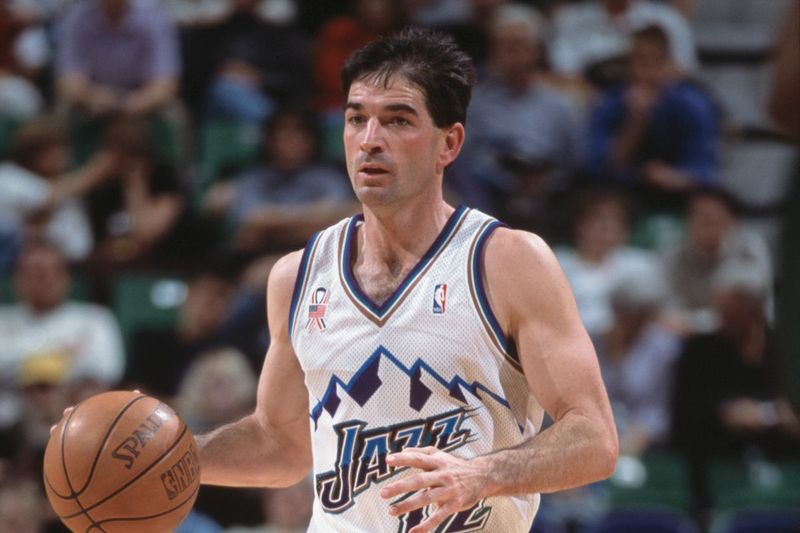 Legend John Stockton was famous in point guard position
Legend John Stockton was famous in point guard position
There have been many famous point guards throughout the history of basketball, each with its own unique play style. For example, Magic Johnson was known for his exceptional court vision and passing ability, while Allen Iverson was a prolific scorer and ball-handler who could take over a game with his speed and quickness. Other notable point guards include Steve Nash, John Stockton, and Chris Paul, all of whom were known for their leadership abilities, playmaking skills, and defensive prowess.
B. Shooting guard
The shooting guard position in basketball is responsible for scoring and playing solid defense. Shooting guards are usually the second shortest player on the team after the point guard, but they often have a more muscular build than point guards. Shooting guards are expected to be strong perimeter shooters, able to score from mid-range and beyond the three-point line. They must also have good ball-handling skills to create scoring opportunities for themselves and their teammates.
On offense, the shooting guard is responsible for creating scoring opportunities for themselves and their teammates. They often move off the ball and look for open spots on the court to receive a pass and shoot. Shooting guards must be able to shoot from different angles, often while on the move, to avoid being closely guarded by defenders. They also need to be good at driving to the basket and finishing with a layup or dunk. Shooting guards are expected to be able to score in a variety of ways, whether from beyond the arc, mid-range jumpers, or attacking the rim.
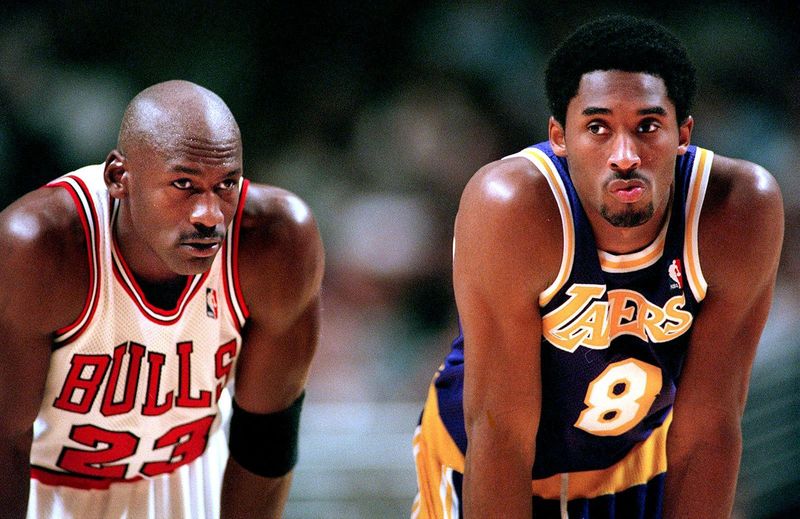 Michael Jordan and Kobe Bryant are notable players
Michael Jordan and Kobe Bryant are notable players
On defense, the shooting guard is responsible for guarding the opposing team's shooting guard and preventing them from scoring. Shooting guards must have good lateral movement and footwork to stay in front of their opponents, contest shots, and prevent open looks. They may also be required to switch and guard other positions, such as small forwards or point guards, depending on the defensive scheme.
Some of the greatest shooting guards in basketball history include Michael Jordan, Kobe Bryant, Dwyane Wade, and James Harden. These players were known for their scoring abilities, including their perimeter shooting and ability to finish at the rim. They also possessed strong defensive skills and were often tasked with guarding the opposing team's best perimeter player.
C. Small forward
The small forward position in basketball is responsible for being a versatile player who can both score and play defense. Small forwards are typically taller and stronger than shooting guards and point guards but are often more mobile than power forwards and centers. They are expected to contribute to both the offense and defense of the team, making them a vital part of any successful basketball team.
On offense, the small forward is responsible for scoring, setting screens, and creating scoring opportunities for their teammates. Small forwards must be able to score from mid-range and beyond the three-point line, and also possess strong ball-handling skills to create their own shots. They are often asked to create mismatches against the opposing team's defense, whether by posting up against smaller defenders or using their speed to drive past slower defenders. Small forwards also contribute to the team's rebounding efforts, as they are often positioned in the key and along the perimeter, allowing them to grab both offensive and defensive rebounds.
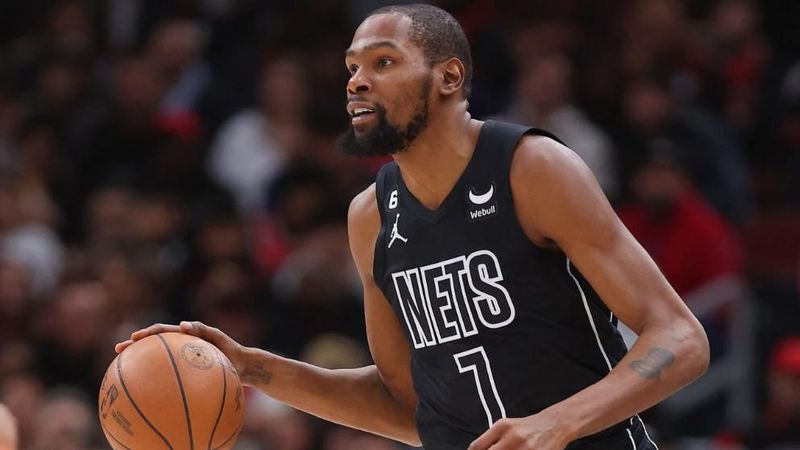 Kevin Durant is an excellent in small foward
Kevin Durant is an excellent in small foward
On defense, the small forward is responsible for guarding the opposing team's small forward and preventing them from scoring. Small forwards must be able to move quickly and laterally, as they often need to guard players who are quick and agile. They must also possess strong defensive skills, such as blocking shots, deflecting passes, and stealing the ball. Small forwards are often involved in defensive rotations and double-team, helping to disrupt the opposing team's offensive flow.
Some of the greatest small forwards in basketball history include LeBron James, Larry Bird, Scottie Pippen, and Kevin Durant. These players were known for their all-around skills, ability to score, rebound, and play solid defense. They were also leaders on the court, able to direct their team's offense and defense to success.
D. Power forward
The power forward position in basketball is responsible for being a strong, physical player who excels at rebounding and defending the key. Power forwards are typically taller and stronger than small forwards, but are often more mobile than centers. They are expected to be a force on both the offensive and defensive ends of the court, making them an important part of any successful basketball team.
On offense, the power forward is responsible for scoring, setting screens, and creating space for their teammates. Power forwards must be able to score from both inside the key and beyond the three-point line. They are often involved in pick-and-roll plays, using their size and strength to set screens for the ball handler. They must also possess strong ball-handling skills, allowing them to create their own shots and drive to the basket. Power forwards are also critical to the team's rebounding efforts, as they are positioned near the key and are often the first to jump for the ball when it comes off the rim.
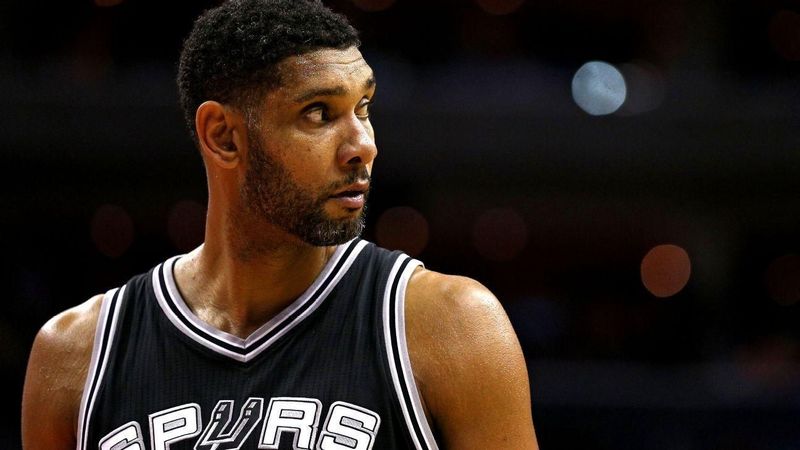 Tim Duncan is incredible power forward
Tim Duncan is incredible power forward
On defense, the power forward is responsible for guarding the opposing team's power forward and center, preventing them from scoring and grabbing rebounds. Power forwards must be able to move quickly and laterally, as they often need to guard players who are both strong and agile. They must also possess strong defensive skills, such as blocking shots, disrupting passes, and stealing the ball. Power forwards are often involved in defensive rotations and double-teams, helping to protect the key and limit the opposing team's scoring opportunities.
Some of the greatest power forwards in basketball history include Tim Duncan, Karl Malone, Charles Barkley, and Kevin Garnett. These players were known for their physicality, their ability to score and rebound, and their strong defensive skills. They were often the backbone of their team, providing both leadership and production on both ends of the court.
E. Center
The center position in basketball is one of the most important roles on the court. The center is typically the tallest player on the team and is responsible for protecting the rim, grabbing rebounds, and scoring points in the key. The center is a pivotal figure in both the team's offensive and defensive strategies.
On offense, the center is responsible for scoring in the paint, setting screens, and passing the ball to open teammates. The center often plays with their back to the basket, receiving passes from guards or forwards and turning to shoot or make a pass. Centers must possess excellent footwork, as they are often double-teamed and must pivot quickly to find an open teammate. Additionally, they must be strong enough to post up and establish positions in basketball
in the key, making it difficult for the opposing team to prevent them from scoring.
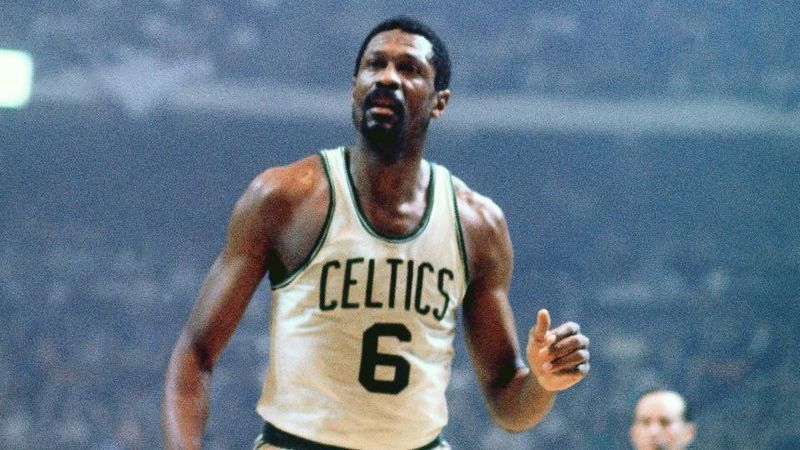 Bill Russell is a legend in the center position
Bill Russell is a legend in the center position
On defense, the center is responsible for protecting the rim and contesting shots. Centers must be agile and quick, able to move quickly to block shots and rebound missed shots. They are also responsible for guarding the opposing team's center and power forward, often switching on screens and making it difficult for the other team to score in the paint.
Some of the greatest centers in basketball history include Wilt Chamberlain, Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Bill Russell, and Shaquille O'Neal. These players were known for their size, strength, and agility, as well as their ability to score and defend the rim. They were often the focal point of their team's offensive and defensive strategies and were considered dominant forces in the game.
III. Other Basketball Positions
A. The sixth man
The sixth man is a position used to describe a player who is the first substitute off the bench. This player is usually one of the team's best players and is used to provide a spark when the starters need a rest or if the team needs a change of pace. The sixth man is typically a player who can play multiple all basketball positions and can contribute in a variety of ways.
The sixth man can be a game-changer for a team, as they bring energy and enthusiasm to the court when they come in. They are often used to lead a team's second unit, which is a group of players who come off the bench together and play against the opposing team's second unit. The sixth man can be a scoring threat, a defensive stalwart, or a facilitator, depending on the team's needs for which basketball positions on court.
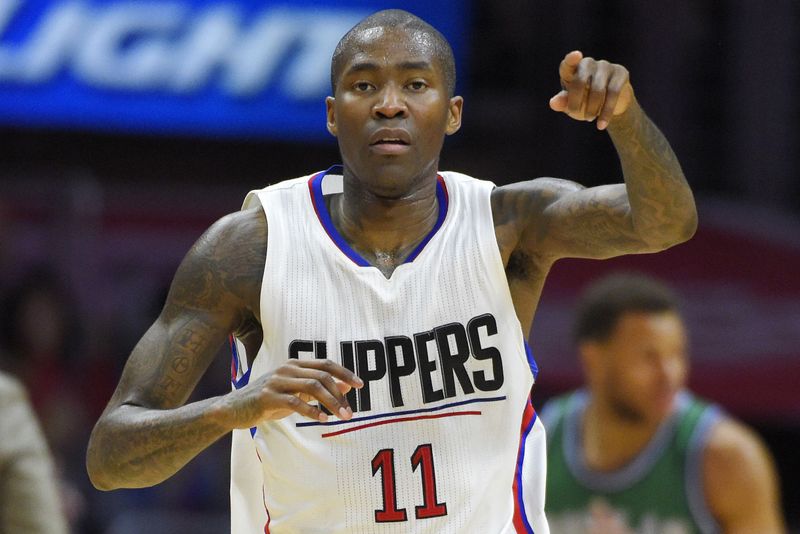

Jamal Crawford
Famous sixth men include Jamal Crawford, Manu Ginobili, and Jason Terry, all of whom were able to make an impact off the bench and lead their teams to success.
B. Combo Guard
The combo guard is a position used to describe a player who can play both point guard and shooting guard positions. Combo guards are often used as a backup to the starting point guard or shooting guard and can provide versatility to a team's lineup.
Combo guards are typically smaller players who are quick and agile, and they can handle the ball and shoot from the outside. They are often used in fast-paced offenses that rely on quick ball movement and penetration into the paint.
Famous combo guards include Dwyane Wade, Damian Lillard, and James Harden, all of whom are known for their ability to play multiple positions and contribute in a variety of ways.
C. Stretch Four
The stretch four is a position used to describe a power forward who has the ability to shoot from the outside. This player is often used to spread the floor and open up driving lanes for the team's guards. The stretch four is typically a taller player who is mobile and can move quickly around the court. They are often used in pick-and-roll situations where they can roll to the basket or pop out for a three-point shot.
Famous stretch fours include Dirk Nowitzki, Kevin Love, and Anthony Davis, all of whom have the ability to score from the outside and stretch the defense.
IV. How Positions Work Together
Basketball is a sport that requires both offensive and defensive strategies in order to win. Teams must work together to execute their game plan, and understanding the different strategies, basketball positions, and roles and how positions work together is essential for success. In this article, we will delve into offensive and defensive strategies in basketball, including how positions work together in different basketball positions and famous teams and their strategies.
A. Offensive Strategies
Offensive strategies in basketball are designed to help a team score points and ultimately win the game. There are many different offensive strategies, and they can vary depending on the team's personnel and the opponent's strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the most common offensive strategies in basketball:
Fast Break
The fast break is an offensive strategy that involves pushing the ball up the court as quickly as possible in order to catch the defense off-guard and score before they have a chance to set up. The point guard usually initiates the fast break by dribbling the ball up the court and passing to a teammate who is running ahead of the defense. The rest of the basketball positions on court follows and looks for opportunities to score before the defense can get set.
Pick and Roll
The pick and roll is an offensive strategy that involves one player setting a screen for another player and then rolling to the basket. The player with the ball can either shoot, pass to the rolling player, or drive to the basket depending on the defense's reaction. This strategy is especially effective if the rolling player is a good scorer or if the defense switches the pick and leaves a mismatch.
Triangle Offense
The triangle offense is a set of offensive principles that focuses on ball movement, player movement, and spacing. It is called the triangle offense because it uses three players in a triangle formation on one side of the court. The triangle offense can be effective because it creates multiple options for the offense and can be difficult for the defense to defend.
Motion Offense
Motion offense is a strategy that emphasizes constant movement and spacing on the court. Players are encouraged to cut, screen, and pass to create open shots and scoring opportunities. The motion offense is effective because it keeps the defense moving and guessing, making it harder for them to defend.
 Offensive strategies is an important part of basketball
Offensive strategies is an important part of basketball
How positions work together to execute offensive plays:
All positions are important in executing offensive plays, but some positions have more responsibility than others. The point guard is usually responsible for initiating offensive plays and getting the ball to the right player at the right time. The shooting guard and small forward are typically the team's primary scorers and will look to create their own shots or take advantage of scoring opportunities created by their teammates. The power forward and center are responsible for setting screens, rebounding, and scoring in the paint.
Famous teams and their offensive strategies:
Many famous basketball teams have had success using offensive strategies. One of the most famous offensive strategies in basketball history is the Triangle Offense, which was used by the Chicago Bulls during the Michael Jordan era. The Golden State Warriors are also known for their offensive prowess and their use of the Motion Offense.
B. Defensive Strategies
Defensive strategies in basketball are designed to prevent the opposing team from scoring and ultimately winning the game. Like offensive strategies, defensive strategies can vary depending on the team's personnel and the opponent's strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the most common defensive strategies in basketball:
Man-to-Man Defense
Man-to-man defense is a strategy where each defender is responsible for guarding one offensive player. The goal is to stay in front of the offensive player and prevent them from scoring. This strategy can be effective if the defenders are quick and agile and can switch assignments on the fly.
Zone Defense
In addition to man-to-man defense, another popular defensive strategy is zone defense. This is where players are assigned to a specific area of the court and are responsible for defending that area. The most common zone defense is the 2-3 zone, where two players are assigned to the front court and three players are assigned to the backcourt. The 2-3 zone is effective in preventing inside shots and forcing the opposing team to take outside shots, which are often lower-percentage shots.
One of the most famous examples of a team that has used a zone defense to great effect is the Syracuse Orange, coached by Jim Boeheim. Boeheim is a master of the 2-3 zone defense and has used it to great effect throughout his coaching career. In fact, the zone defense is often referred to as the "Syracuse zone" because of the team's success with it.
 Defensive strategies are no less crucial than offensive ones
Defensive strategies are no less crucial than offensive ones
Understanding the different basketball positions is crucial for any fan, player, or coach. Each position has its own unique set of roles and responsibilities, and they must work together in order to form a cohesive team. The point guard is responsible for directing the offense, while the shooting guard is primarily a scorer. The small forward is a versatile player who can both score and defend, while the power forward is responsible for rebounding and playing inside. The center is typically the tallest player on the team and is responsible for playing inside and defending the rim.
In addition to these five traditional positions, there are also other positions such as the sixth man, combo guard, and stretch four. These positions may not be as well-known as the traditional positions in basketball, but they are still important for a team's success. Finally, understanding offensive and defensive strategies is also important for any basketball player, fan, or coach. Teams use a variety of offensive strategies such as pick-and-roll, motion offense, and triangle offense. On defense, teams can use man-to-man defense or zone defense to prevent the opposing team from scoring. By understanding the different positions and strategies in basketball, fans, players, and coaches can gain a greater appreciation for the game and become more knowledgeable about what it takes to win.
V. Frequently Asked Questions
Here are the answers to some commonly asked questions about basketball positions and the game itself:
What are the 5 positions in basketball?
The five traditional positions in basketball are: point guard, shooting guard, small forward, power forward, and center.
What are the 4 and 5 positions in basketball?
The 4 and 5 positions in basketball refer to the power forward and center positions, respectively. These different basketball positions are usually the tallest and strongest players on the team, responsible for rebounding, defending the basket, and scoring inside.
What is each position in basketball?
Each basketball position has its own unique role and responsibilities:
Point guard: primary ball-handler, responsible for initiating the offense and setting up plays.
Shooting guard: typically the team's best perimeter scorer, responsible for shooting from outside and driving to the basket.
Small forward: a versatile player who can score from anywhere on the court and defend multiple positions.
Power forward: a strong player who can score inside and rebound, often playing close to the basket.
Center: tallest player on the team, responsible for defending the basket, rebounding, and scoring close to the rim.
Who can play all 5 positions in basketball?
It is rare for a player to be skilled enough to play all five different basketball positions effectively, but some players have been known to do so. One such player is LeBron James, who has played all five positions at various times in his career.
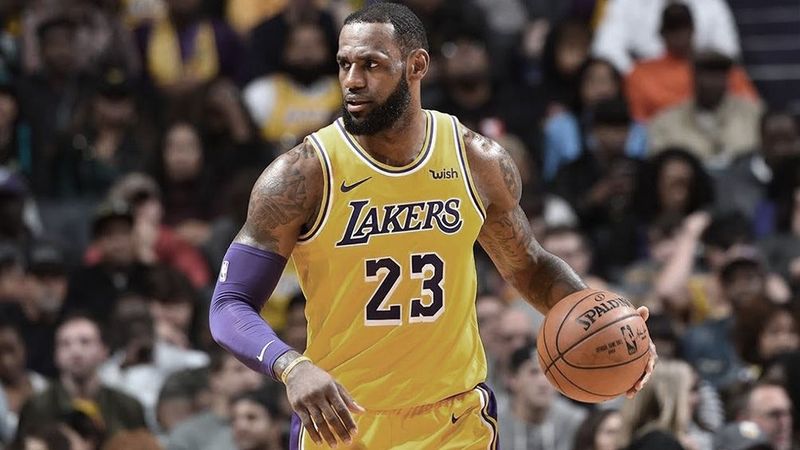 LeBron James can play in 5 different positions
LeBron James can play in 5 different positions
What are the 6 types of passes in basketball?
The six types of passes in basketball are chest pass, bounce pass, overhead pass, one-handed pass, behind-the-back pass, and no-look pass.
How long is a basketball game?
A standard basketball game consists of four quarters, each lasting 12 minutes at the professional level. However, the duration of a game can vary depending on the level of competition and the specific rules being followed.
What does PG mean in basketball?
PG stands for a point guard in basketball. The point guard is one of the positions in basketball that is responsible for initiating the offense and setting up plays.
Is a high-five a foul in basketball?
No, a high five is not a foul in basketball. It is a common gesture of celebration or encouragement among teammates, coaches, and fans. However, if a player high-fives an opponent during play, it could be considered unsportsmanlike conduct and result in a technical foul.

Related Content


























